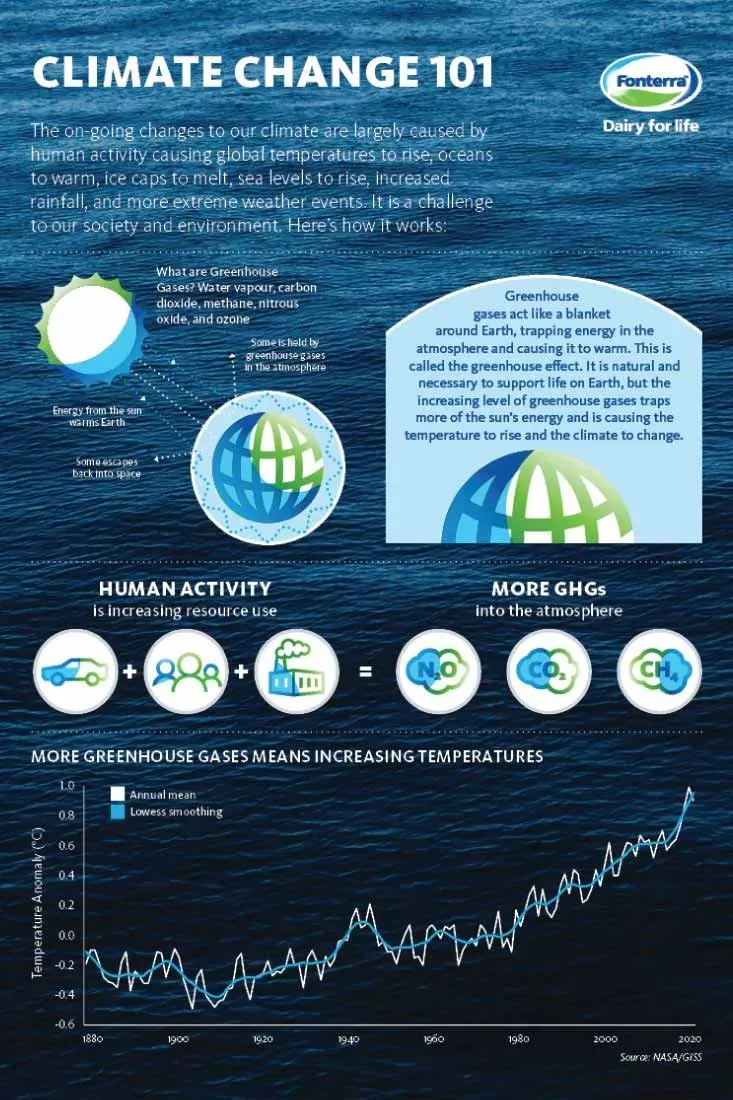
Climate Change 101 offers a practical map to understanding how our planet is changing and why these shifts matter to you, your community, and the economy. This guide clarifies climate change basics and clarifies climate change explained in plain terms so you can separate science from sensational headlines. It also explains what causes climate change—the human activities that release greenhouse gases and alter landscapes. Understanding the effects of climate change helps people anticipate impacts on health, agriculture, and coastal communities. Armed with this knowledge, you can take informed, practical steps at home and in your community to reduce emissions and build resilience, and understand why climate change matters for future generations and current policy choices.
Climate Change 101: What It Is, What Causes Climate Change, and Climate Change Basics
Climate Change 101 provides a concise map of the science that underpins climate change basics. In plain language, climate change explained describes how human activities are increasing greenhouse gas concentrations and nudging global average temperatures higher. This section sets the foundation so readers can recognize the key elements: the difference between weather and climate, the long-term trends, and the relevance of data and evidence.
Beyond definitions, understanding what causes climate change helps turn knowledge into action. The main drivers include burning fossil fuels for energy and transportation, deforestation that reduces carbon sinks, and certain industrial processes that release methane, nitrous oxide, and other pollutants. Natural factors can modulate warming, but the rapid pace of recent change is strongly linked to human actions, highlighting why climate change basics and what causes climate change matter for effective solutions.
Why Climate Change Matters: Effects of Climate Change on Health, Economies, and Ecosystems
Why Climate Change Matters: The effects of climate change are felt across health, water availability, food security, and economic activity. Hotter heat waves stress health systems; heavier rainfall and flooding disrupt infrastructure; droughts threaten crops and water supplies. Coastal communities face rising sea levels and increased storm intensity, while ecosystems shift and species adapt or retreat. These effects of climate change are interconnected, creating risks that touch individuals, families, and national economies alike.
Addressing these challenges requires both mitigation and adaptation. The climate change explained angle shows how reducing emissions, expanding clean energy, and protecting forests can slow warming, while resilience planning and targeted policies help communities withstand impacts. Individuals can act through energy choices, transportation, and advocacy, while governments and businesses align incentives to accelerate clean technology and sustainable practices. When people understand why climate change matters and how the science translates into daily decisions, collective action becomes both feasible and urgent.
Frequently Asked Questions
Climate Change 101: What are the climate change basics and what causes climate change?
Climate Change 101 introduces the long-term shift in Earth’s average weather, i.e., climate change basics. It explains that the primary what causes climate change are human activities—burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and certain industrial processes—that raise greenhouse gas concentrations. Greenhouse gases trap heat, driving warming, while natural factors can modulate the trend. Understanding these elements helps individuals and communities pursue emissions cuts and stronger resilience.
Why climate change matters: How Climate Change 101 explains the effects of climate change on people and ecosystems
In climate change explained terms, Climate Change 101 connects science to daily life by outlining the effects of climate change—from heat waves and storms to water shortages and crop risks. These changes affect health, economies, and biodiversity, with vulnerable communities often bearing the highest burden. Climate Change 101 also highlights actions to reduce emissions, switch to clean energy, and build resilience, underscoring why climate change matters for everyone.
| Key Point | Summary |
|---|---|
| What is Climate Change 101? | Long-term shift in average weather patterns driven largely by human activities (greenhouse gases, burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and certain industrial processes); natural factors can modulate warming, but the current pace is human-driven. |
| The Science Behind Climate Change Explained | Greenhouse gases trap heat, forming a blanket around the planet. CO2, CH4, N2O, and fluorinated gases contribute to warming; burning fossil fuels releases these gases; deforestation reduces CO2 absorption; the result is a warming trend reflected in long-term patterns rather than single events. |
| Evidence and Impacts | Global surface temperatures have risen; glaciers and ice sheets retreat; sea levels rise; precipitation patterns shift; more intense heat waves, heavier rainfall, and longer droughts are observed, affecting food security, health, and economies. |
| Why It Matters | Shifts in climate affect crops, disease vectors, and natural cycles essential to industries like farming and tourism. Vulnerable populations—low-income communities, small island nations, and drought- or flood-prone regions—bear the brunt. Biodiversity loss impacts ecosystem services such as pollination, clean water, and storm protection. |
| From Concepts to Action | Mitigation reduces emissions; adaptation prepares for changes. Practical steps include evaluating your carbon footprint, adopting energy-efficient appliances, using renewables, opting for low-carbon transport, reducing meat consumption, and supporting clean-energy policies. Community actions (local clean-energy projects, tree planting, resilience planning) reinforce everyday impact. |
| Key Concepts in Everyday Terms | – Greenhouse gases trap heat, driving warming. – Fossil fuels are a major source of CO2 and methane. – Land use and forestry influence carbon balance. – Climate change affects more than temperature (weather, water, health, infrastructure). – Equity matters; vulnerable communities need inclusive policies. |
| Practical Steps for Individuals and Communities | – Reduce energy use at home with efficient appliances, insulation, and renewables where feasible. – Move toward low-carbon transportation (walk, bike, transit, carpool; consider electric/hybrid vehicles). – Adjust consumption (durable goods, repair, reduce food waste; plant-forward meals). – Support policies and practices that favor clean energy and sustainability. – Invest in resilience (infrastructure, flood defenses, heat mitigation). – Educate and engage (talk about climate change explained, participate in local planning, vote for climate solutions). |
| Bringing It All Together | Climate Change 101 connects science to action, emphasizing that knowledge should translate into reduced emissions, better adaptation, and equitable, science-based strategies that protect people and ecosystems. Individual and collective efforts compound to drive meaningful progress. |
Summary
Climate Change 101 is a practical guide to understanding how human activities alter the Earth’s climate and why these changes matter to people, communities, and economies. By presenting the basics, the science behind it, the evidence and impacts, and actionable steps, Climate Change 101 helps readers grasp urgency and find concrete ways to contribute to a more sustainable future. From reducing emissions at home to supporting resilient communities and responsible policies, Climate Change 101 lays out a vision where knowledge leads to informed choices and real impact.